ACN (Australian Company Number) and ABN (Australian Business Number) are two identifying numbers that serve very different purposes. While every Australian business needs an ABN, only businesses registered as companies require an ACN.
For someone about to start up a business, or who is considering what structure is going to be most appropriate for their business needs, it’s important to understand what the two different numbers represent, how to apply for them, the difference between the two and the benefits which each can bring.
Pherrus Financial Services is a leading Australian provider of accountancy, wealth creation and business management services. Get in touch with us to find out more about ACN/ABN, or for any other business accounting related query.
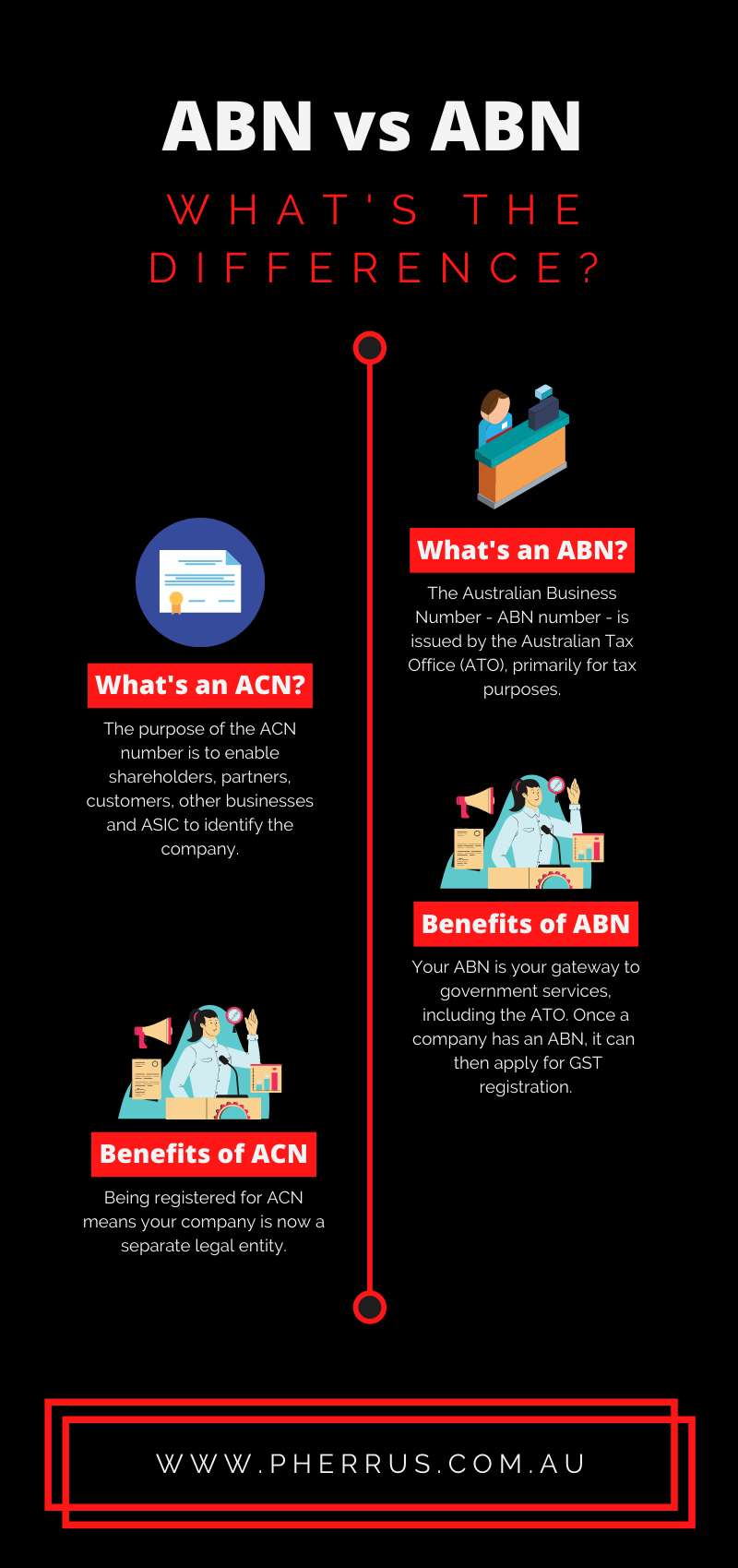
What is ACN ?
What is an ACN number? We’ve given the answer to this commonly asked question below:
The Australian Company Number (ACN) is a unique, 9-digit number that’s issued to a company as soon as it’s registered.
The ACN is issued by ASIC (the Australian Securities and Investments Commission) once registration of the company with them is complete.
Note that an ACN is only issued if a company (with a corporate structure) is registered with ASIC: other business models which aren’t companies (such as freelancers, self-employed individuals or trusts, for example) don’t need an ACN.
The purpose of the ACN number is to enable shareholders, partners, customers, other businesses and ASIC to identify the company.
The ACN can also be used to search for information on a company; for example, an ACN is proof that a company is an incorporated entity.
The ACN company identifier must appear on all documentation pertaining to the company, as well as its online/digital information. This includes:
- Company stationery, including invoices, receipts, estimates and similar
- Any information that’s required by ASIC
- Advertisements
- Orders for goods or services
- Company website or anywhere that the company will reasonably be expected to be finding customers.
How do I get an ACN ?
A company is given an ACN once it has registered with ASIC as a company. To do this, it’s first necessary to decide that a company structure is going to be the most appropriate way for your business to operate.
If you’re not sure of the pros and cons of the various structures available, it’s worth discussing the decision with experienced, professional accountants who will be able to offer the best advice for your enterprise.
Once you’ve decided that becoming a company is the right way forward for your business, you’ll need to decide on a company name and put in place a suitable corporate structure.
You’ll also need to let interested individuals or organisations know that your business is going to become a company and alert them to the changes in your company structure.
It’s also important to understand your corporate responsibilities: operating as a company requires the fulfilment of a number of tasks, many of which are specific to having a corporate structure.
By way of example, this can include preparing quarterly or monthly Business Activity Statements (BAS) and submitting them to the ATO (Australian Tax Office). A task that professional bookkeepers and accountants can assist with, in preparation for your tax obligations.
As soon as these steps have been completed, you can apply to ASIC for company status. Once it’s been granted you will be issued with an ACN Australia companies use to identify themselves.
What is an ABN ?
The Australian Business Number – ABN number – is issued by the Australian Tax Office (ATO), primarily for tax purposes. Any enterprise that is trading as a business (including companies, trusts, sole traders, partnerships and not-for-profit companies) is required to register with the ATO for an ABN number.
The ABN number is an 11-digit number that’s issued by the ATO once you’ve registered with them as a (potentially) tax-paying business.
The process is straight forward and can be completed entirely online. Once registered with the ATO, you will be issued with your ABN number. The ABN number is used by the ATO to keep track of tax responsibilities and related business matters.
Once your business has an ABN, you can then apply to the ATO for further tax registrations (such as GST), Goods and Services Tax.
A little like the ACN, the ABN needs to be displayed on all your business correspondence.
Documents, where it will need to be displayed, include :
- Invoices
- Receipts
- Estimates
- Orders
- Tax returns
- BAS
- Statement of accounts
- Letterheads
- Any other official form of business communication
ABN vs ACN: What is the difference between ABN and ACN ?
There are several key differences between the two :
- ACN is only needed by a company
- ABN is needed by any Australian business, regardless of its structure, including companies
- ACN is issued by ASIC, whilst the ABN is issued by the ATO
What are the benefits of ACN ?
ACN Australia provides a number of advantages, which include :
- Required for legal compliance.
- Enables shareholders, partners, and other interested parties to obtain information about the company.
- An ACN is proof of ASIC registration: it’s often used by potential customers to determine if a company is a bona fide business.
- Is accepted as proof that the company is who they say they are
- for example when ordering from a new supplier.
- Being registered for ACN means your company is now a separate legal entity.
Particularly if you’ve moved away from the sole trader model to incorporate your business, the corporate structure can represent a significant reduction in trading risk and personal liability, as well as potentially increase your profitability.
Pherrus Financial Services is a highly experienced group of consultants, accountants and business experts offering a one-stop financial and management solution for businesses of all shapes and sizes including bookkeeping in Sydney.
Get in touch to find out more about the ACN and the ABN, as well as additional insight into the pros and cons of your business becoming incorporated.
What are the benefits of ABN?
The ABN confers the following advantages :
- It enables businesses to be easily recognised, as it’s unique to the business.
- Once a company has an ABN, it can apply for GST registration.
- If you don’t need to pay tax (for example, if you’re a charity), your ABN is needed to confirm your charitable status.
- Your ABN is your gateway to government services, including the ATO
For more information see our infographic below.